Palm oil disadvantages: why the topic requires attention? Are health issues serious enough, or are users of palm oil conscious? If we ask, most of the population replies that they don’t use palm oil, yes! It’s not in your kitchen but in your routine.
Palm oil is the most widely used vegetable oil globally, accounting for approximately 36% of all vegetable oils produced. Let’s discover how silently palm oil dominates our lives and makes us addicted to it.
Palm oil
What is palm oil? Palm oil is a vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of oil palms.
Palm oil from pulp has two varieties, one is red, which is non-refined, and the other is processed and refined.
The nutritional value of Red Palm Oil vs Refined Palm Oil per 1 tablespoon (approx. 14 grams):
| Nutrient | Red Palm Oil | Refined Palm Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | ~120 kcal | ~120 kcal |
| Total Fat | 14 g | 14 g |
| └ Saturated Fat | ~6.7 g | ~6.7 g |
| └ Monounsaturated Fat | ~5.0 g | ~5.0 g |
| └ Polyunsaturated Fat | ~1.3 g | ~1.3 g |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0 mg |
| Vitamin A (from carotenoids) | 10,000–15,000 IU (rich source) | Negligible (mostly lost during refining) |
| Vitamin E (Tocotrienols & Tocopherols) | High (rich in tocotrienols) | Moderate (reduced during refining) |
| Color | Reddish-orange (due to beta-carotene) | Pale yellow to colorless |
| Antioxidants | High | Low |
| Processing | Cold-pressed, minimally processed | Heavily refined, bleached, deodorized |
-
Red palm oil is rich in carotenoids (provitamin A) and vitamin E (tocotrienols). High heat destroys these antioxidants.
-
Prolonged or repeated high-heat cooking can cause red palm oil to oxidize, forming free radicals that promote inflammation.
- Heating beyond its smoke point (~230°C) or using it repeatedly can lead to partial breakdown into trans fats, which are harmful to heart health.
- Palm oil is high in saturated fat, which may raise LDL cholesterol and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
How do we eat palm oil unknowingly?
- Palm oil is often listed as an edible oil blend or a vegetable oil, found in biscuits, cookies, instant noodles, chips, cake, chocolates, and spreads.
- Street foods and fast food chains mostly use and reuse palm oil.
- In ultra-processed foods like ice cream, bread buns, breakfast cereals, and cream-filled biscuits.
- Non-food sources like lipstick, toothpaste often contain palm derivatives palmitate, which may be swallowed and add up overall palm oil exposure.
- The labels use confusing names, palm olein, stearin, sodium laurate sulfate, and glyceryl stearate.
Palm Oil Disadvantages
1. Cholesterol levels
- Palm oil is high in saturated fats and can increase bad cholesterol (LDL).
- Increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and blocked arteries.
2. Increase inflammation
- Refined palm oil can activate the inflammatory pathway.
- may worsen insulin resistance.
3. Weight gain and fat storage
- High calorie density.
- Palm oil gives food a buttery, creamy mouthfeel, enhancing sensory pleasure, which reinforces habitual overconsumption.
- Unknowingly eating leads to obesity.
4. Triggers overeating
- High-fat and high-sugar food made with palm oil overrides satiety signals
- This leads to mindless eating.
5. Harmful Compounds Formed by Palm Oil
-
AGEs, trans fats, Glycidyl Fatty Acid Esters(GE), Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
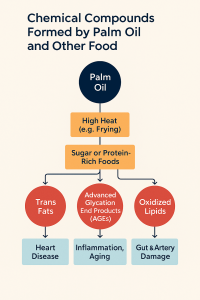
Chemical Compound How It’s Formed Effect on Body Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) When palm oil is cooked at high heat with sugar or proteins (e.g., frying breaded fo ods, pastries)
Promote inflammation, aging, and damage to blood vessels, skin, and organs. Trans Fats When palm oil is partially hydrogenated (common in processed foods) Raise LDL (bad) cholesterol, lower HDL (good), increase heart disease risk Glycidyl Fatty Acid Esters (GE) Formed when palm oil is refined at high temperatures Can release glycidol, a potential carcinogen Oxidized Lipids Reheating palm oil during deep-frying causes oxidation Causes cell damage, inflammation, and may worsen metabolic disorders. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Palm oil + high sugar diet = oxidative stress Leads to DNA damage, aging, and chronic disease development
Palm Oil and the Dopamine Trap
Palm oil itself is not chemically addictive like nicotine or caffeine, but it plays a strong role in food addiction because of how it interacts with the brain and body, especially when combined with sugar, salt, and refined carbs.


Good health awareness article.
Hey, I just stumbled onto your site… are you always this good at catching attention, or did you make it just for me? Write to me on this website — rb.gy/ydlgvk?Bab — my username is the same, I’ll be waiting.